
Menopause encompasses more than just hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. Despite being a common phase affecting roughly half of the population, menopause is often misunderstood, both by the public and many healthcare providers. This gap in knowledge can lead to unnecessary suffering, as many individuals are not fully informed about effective treatments.
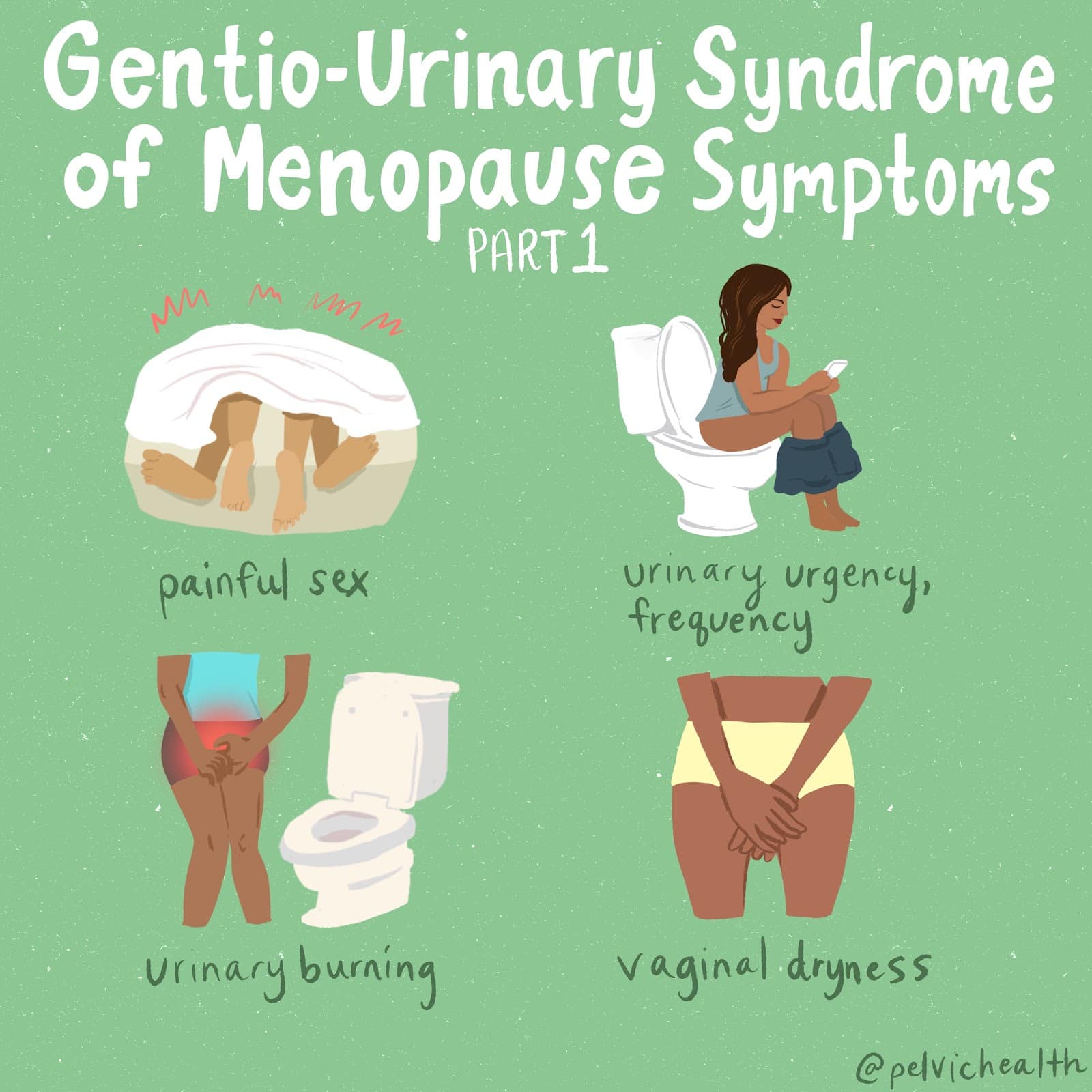
Perimenopause, the transitional phase leading up to menopause, typically begins in a person’s 40s, with menopause itself usually occurring in the early 50s. While systemic symptoms like hot flashes and mood changes are well-known, many people also experience less obvious but equally impactful genitourinary symptoms. These can include painful intercourse, urinary urgency, frequent urination, leakage, burning sensations, recurrent vaginal and urinary tract infections, and vaginal dryness. Collectively, these symptoms are part of the Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM). Additionally, many women experience pelvic floor dysfunction, which affects nearly 50% of women by their 50s and can overlap with GSM symptoms.
While systemic hormonal therapy is commonly used to manage menopause symptoms, it may not address the specific needs of those experiencing GSM. The North American Menopause Society recommends the use of vaginal estrogen as an effective treatment for alleviating GSM symptoms and improving quality of life.
Menopause encompasses more than just hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. Despite being a common phase affecting roughly half of the population, menopause is often misunderstood, both by the public and many healthcare providers. This gap in knowledge can lead to unnecessary suffering, as many individuals are not fully informed about effective treatments.
Perimenopause, the transitional phase leading up to menopause, typically begins in a person’s 40s, with menopause itself usually occurring in the early 50s. While systemic symptoms like hot flashes and mood changes are well-known, many people also experience less obvious but equally impactful genitourinary symptoms. These can include painful intercourse, urinary urgency, frequent urination, leakage, burning sensations, recurrent vaginal and urinary tract infections, and vaginal dryness. Collectively, these symptoms are part of the Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM). Additionally, many women experience pelvic floor dysfunction, which affects nearly 50% of women by their 50s and can overlap with GSM symptoms.
While systemic hormonal therapy is commonly used to manage menopause symptoms, it may not address the specific needs of those experiencing GSM. The North American Menopause Society recommends the use of vaginal estrogen as an effective treatment for alleviating GSM symptoms and improving quality of life.
Differential Diagnosis:
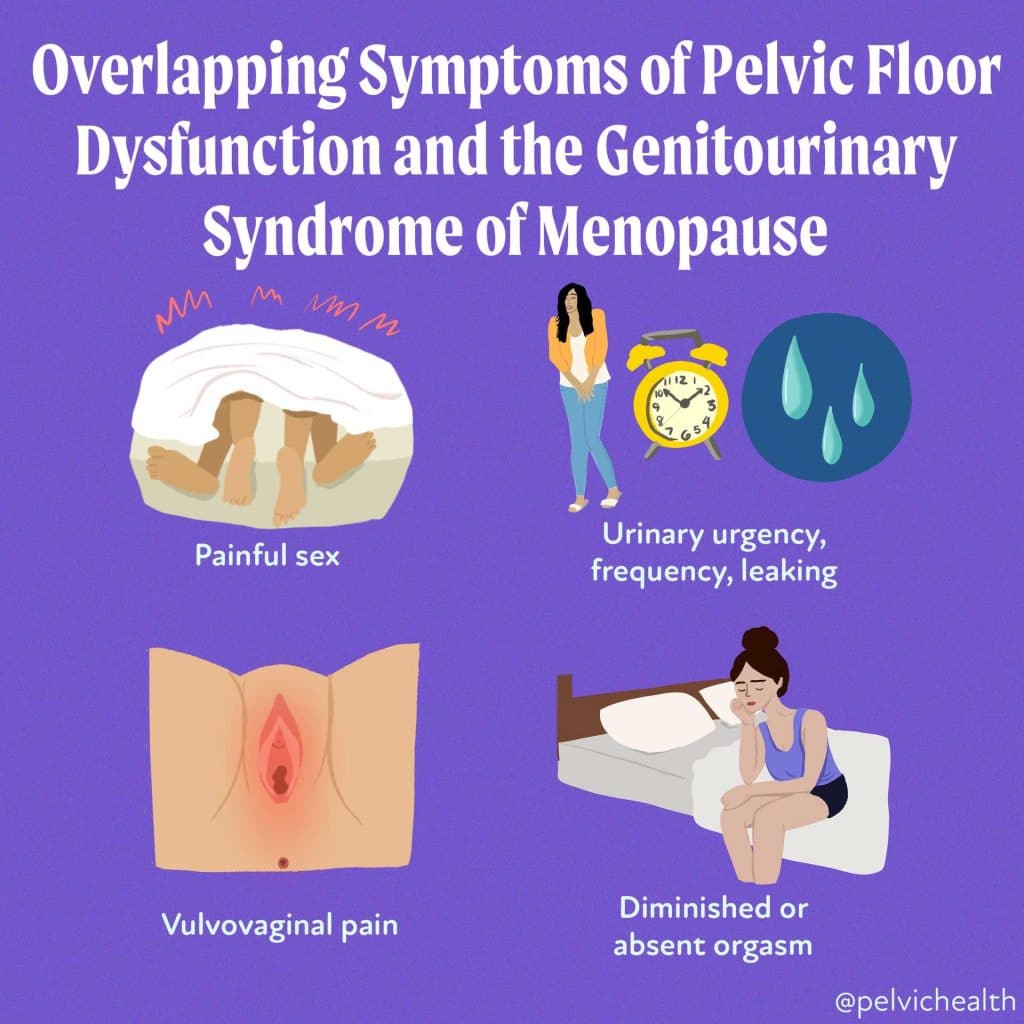
GSM or Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction and Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) can overlap and include:
- Urinary urgency, frequency, burning, nocturia
- Feelings of bladder or pelvic pressure
- Painful sex
- Diminished or absent orgasm
- Difficulty evacuating stool
- Vulvovaginal pain and burning
- Pain with sitting
An experienced healthcare provider, whether a pelvic floor physical and occupational therapists or a medical doctor, can conduct several assessments to diagnose pelvic floor dysfunction, hormonal deficiencies, and pelvic organ prolapse. These evaluations include a vulvovaginal visual examination, a Q-tip test to pinpoint areas of pain, and a digital manual examination.
Without appropriate medical management, all women may eventually experience symptoms of Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM). Many are unaware that a pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy evaluation can be highly beneficial for addressing the musculoskeletal issues contributing to their discomfort. Combining pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy with medical treatments can be crucial for improving sexual enjoyment and resolving urinary and bowel problems.
Virtual pelvic floor therapy for menopause—contact us to get started!
FACTS
From: https://www.letstalkmenopause.org/further-reading
- Every day, approximately 6,000 women reach menopause.
- In the United States, around 50 million women are currently navigating menopause.
- About 84% of women experience genital, sexual, and urinary discomfort related to menopause, which often does not resolve without intervention, yet fewer than 25% seek assistance.
- An estimated 80% of OB-GYN residents acknowledge feeling inadequately prepared to address menopause-related issues.
- Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) is clinically identified in 90% of postmenopausal women, yet only one-third report experiencing symptoms in surveys.
- Barriers to treatment include women needing to initiate discussions about their symptoms, a belief that these issues are simply part of aging, and a failure to connect symptoms with menopause.
- Only 13% of healthcare providers routinely inquire about menopause-related symptoms with their patients.
- Even after a diagnosis of GSM, many women remain untreated. This is partly due to healthcare providers’ reluctance to prescribe treatments and patients’ concerns about the safety of topical vaginal therapies, despite evidence showing that GSM significantly affects quality of life.
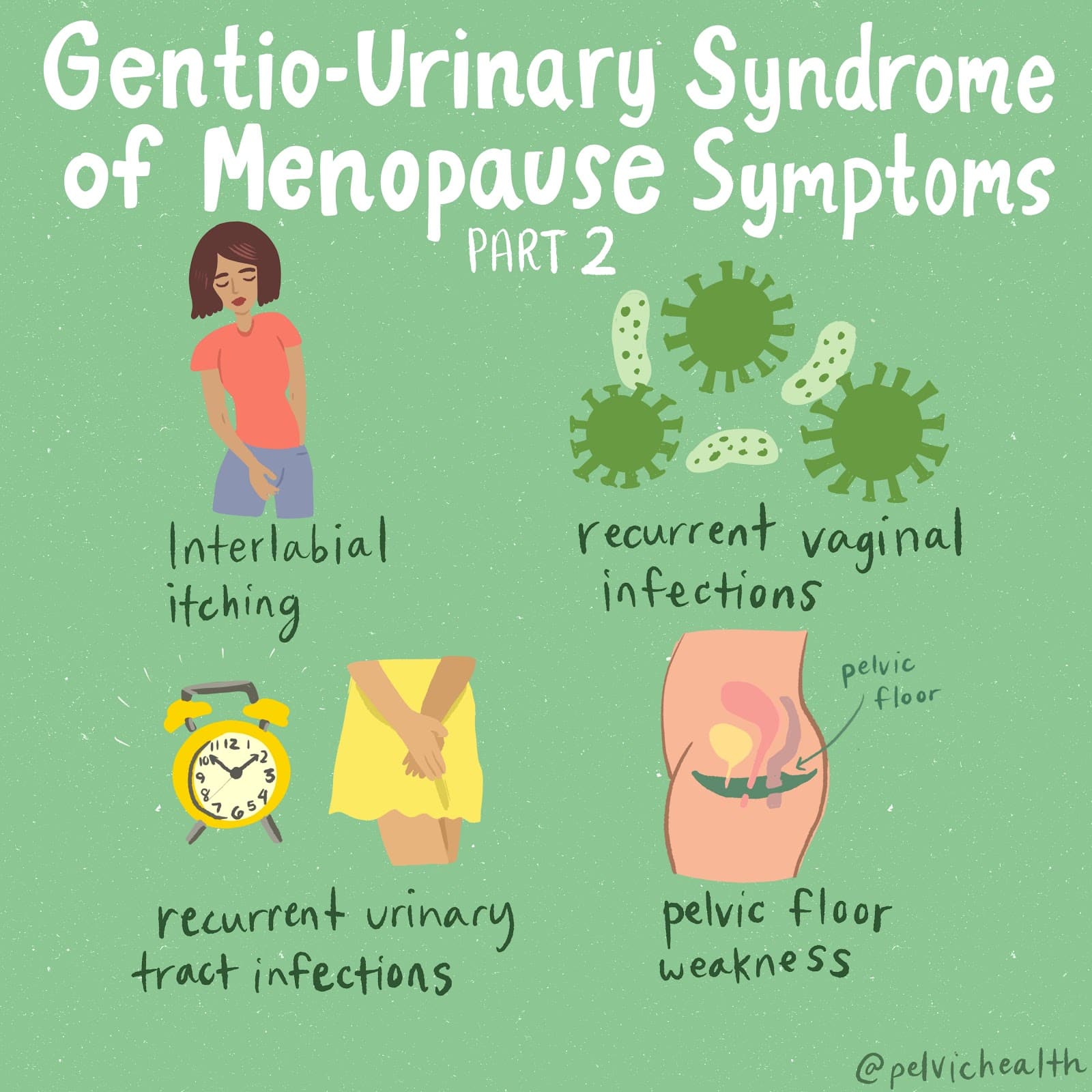
Hormone deficiency can lead to itching in the labial and vaginal areas. Additionally, other dermatological conditions, such as Lichen Sclerosus and cutaneous yeast infections, should also be considered.
During menopause, individuals are particularly susceptible to frequent vaginal and urinary tract infections due to:
- pH and tissue changes
- incomplete bladder emptying
- pelvic organ prolapse compromising urinary function
Recurrent infections are a major contributor to pelvic floor dysfunction. It’s crucial to address these infections promptly, as ongoing visceral-somatic input from untreated infections can lead to increased pain and further dysfunction even after the infection has been resolved. Without appropriate hormone therapy, infections may persist, leading to severe consequences. Untreated infections can cause unprovoked pain, make sexual activity difficult or impossible, and undiagnosed urinary tract infections (UTIs) may progress to kidney issues and other serious complications.
We recommend consulting with a menopause specialist to effectively monitor, prevent, and treat Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) since these issues are both significant and manageable. It’s important to normalize discussions about GSM; there’s no need for embarrassment. With appropriate care, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Combining virtual pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy with medical management is essential for optimal results.
Treatment:
How We Can Help You
If you’re experiencing sexual dysfunction, it’s beneficial to consult a pelvic floor physical and occupational therapists online. They can assess whether any issues with your pelvic floor are contributing to your symptoms. During your initial virtual evaluation, the therapist will review your medical history, including previous diagnoses, treatments, and their effectiveness. They understand that many patients feel frustrated by the time they seek help.
The therapist will examine your nerves, muscles, joints, tissues, and movement patterns. After the assessment, they will discuss the findings with you and set both short-term and long-term therapy goals. Typically, physical and occupational therapy sessions occur once or twice a week over a period of approximately 12 weeks. Your therapist will also coordinate with other specialists on your treatment team and provide you with a personalized home exercise program. Our goal is to support your recovery and help you achieve the best possible quality of life.
Get virtual pelvic floor therapy for menopause. Book your online consultation today!

Treatment:
How We Can Help You
If you are having issues with your sexual function, it is in your best interest to get evaluated by a therapist for pelvic floor therapy, so they can establish what part, if any, of your pelvic floor may be contributing to the symptoms you are experiencing. During the course of the examination, the physical and occupational therapists will talk to you about your medical history and symptoms, including what you have been previously diagnosed with, the treatments or therapies you have had, and how effective or ineffective these therapies have been for you. It is significant to mention that we fully comprehend what you’ve been dealing with and that the majority of individuals are angry by the time they make it to see us. The physical and occupational therapists will conduct an evaluation of the patient’s nerves, muscles, joints, tissues, and movement patterns while doing the physical examination. After the examination is finished, your therapist will go over the results of the assessment with you. The physical and occupational therapists will conduct an evaluation to determine the cause of your symptoms and will establish both short-term and long-term therapy goals based on the results of the evaluation. Physical therapy treatments are typically administered between once and twice each week for a period of around 12 weeks. Your physical and occupational therapists will assist you in coordinating your recovery with all the other experts on your treatment team. They will provide you with an exercise regimen to complete at home and the sessions you attend in person. We are here to assist you in getting better and living the best life possible.
Get virtual pelvic floor therapy for menopause. Book your online consultation today!
By PHRC Admin
The human body is an intricate masterpiece, and within its depths lies a source of immense pleasure and connection: the pelvic floor muscles. Often overlooked or underestimated, these muscles play a vital role in sexual arousal and orgasm. In this blog post, we will explore the wonders of the pelvic floor muscles and how understanding and harnessing their power can enhance your pleasure journey.
Understanding the Pelvic Floor:
The pelvic floor is a network of muscles that forms the base of the pelvis. It supports the pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus, and rectum. However, its significance extends far beyond structural support. During sexual arousal and orgasm, the pelvic floor muscles come alive, creating a symphony of sensations that can take your pleasure to new heights.
The Role of Pelvic Floor Muscles in Orgasm:
- Pubococcygeus (PC) and Iliococcygeus Muscles: Located from the pubic bone to the tailbone and rim of the pelvic to the tailbone (respectively), these muscles are key players in orgasmic bliss. As arousal intensifies, these muscles contract rhythmically during orgasm, adding depth and intensity to the experience. Strengthening and relaxing these muscles through exercises like pelvic floor contractions can enhance their responsiveness and amplify pleasure.
- Bulbospongiosus Muscle:The bulbospongiosus muscle surrounds the vaginal opening and goes up to the base of the clitoris. It also travels from the perineum to the base of the penis. During orgasm, it contracts, contributing to the pleasurable contractions and adding an extra dimension of ecstasy. It also helps to narrow the urethra, like a sphincter, to prevent incontinence.
- Ischiocavernosus Muscle: Residing along the sides of the pelvic floor, the ischiocavernosus muscle plays a multifaceted role. It helps maintain penile and clitoral erections and it contributes to the rhythmic contractions experienced during orgasm.
- Puborectalis Muscle: While primarily involved in maintaining bowel control, the puborectalis muscle can also make its presence known during orgasm. Involuntary contractions can enhance pleasure and intensify the overall experience.
Embracing Your Pleasure:
Exploring and understanding your own body is a deeply personal and empowering journey. Here are some tips to help you embrace the power of your pelvic floor muscles and enhance your pleasure:
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Engaging in pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen and relax these muscles. We recommend checking in with your pelvic floor physical and occupational therapists to be evaluated and prescribed exercises specific to the state of your pelvic floor.
- Mind-Body Connection: Developing a strong mind-body connection can heighten sensitivity and pleasure. Practice mindfulness and focus on sensations during intimate moments. Pay attention to how your pelvic floor muscles respond and learn to engage and relax them consciously.
- Communication and Exploration: Open communication with your partner(s) about desires, boundaries, and preferences can create a supportive and enriching sexual experience. Explore different positions, techniques, and sensations together to discover what works best for you. Working with a Sex Therapist can help couples learn how to do this better!
The pelvic floor muscles hold incredible potential for pleasure and connection. By understanding their role and engaging in exercises (as appropriate per your specific pelvic floor health) and harnessing their power, you can embark on a transformative pleasure journey. Remember, everyone’s experience is unique, so take the time to explore and celebrate your body’s capacity for pleasure. Embrace the power of your pelvic floor muscles, and let them guide you to new heights of ecstasy and fulfillment.
Sources:
- Mayo Clinic: Kegel Exercises for Men: Understand the Benefits
- Healthline: How to Do Kegel Exercises for Men
- Healthline: Pelvic Floor Muscles: Anatomy, Function, and Exercises
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Are you unable to come see us in person in the Bay Area, Southern California or New England? We offer virtual physical and occupational therapy appointments too!
Virtual sessions are available with PHRC pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss via our video platform, Zoom, or via phone. For more information and to schedule, please visit our digital healthcare page.
Do you enjoy or blog and want more content from PHRC? Please head over to social media!
FAQ
What are pelvic floor muscles?
The pelvic floor muscles are a group of muscles that run from the coccyx to the pubic bone. They are part of the core, helping to support our entire body as well as providing support for the bowel, bladder and uterus. These muscles help us maintain bowel and bladder control and are involved in sexual pleasure and orgasm. The technical name of the pelvic floor muscles is the Levator Ani muscle group. The pudendal nerve, the levator ani nerve, and branches from the S2 – S4 nerve roots innervate the pelvic floor muscles. They are under voluntary and autonomic control, which is a unique feature only they possess compared to other muscle groups.
What is pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy?
Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy is a specialized area of physical and occupational therapy. Currently, physical and occupational therapistss need advanced post-graduate education to be able to help people with pelvic floor dysfunction because pelvic floor disorders are not yet being taught in standard physical and occupational therapy curricula. The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center provides extensive training for our staff because we recognize the limitations of physical and occupational therapy education in this unique area.
What happens at pelvic floor therapy?
During an evaluation for pelvic floor dysfunction the physical and occupational therapists will take a detailed history. Following the history the physical and occupational therapists will leave the room to allow the patient to change and drape themselves. The physical and occupational therapists will return to the room and using gloved hands will perform an external and internal manual assessment of the pelvic floor and girdle muscles. The physical and occupational therapists will once again leave the room and allow the patient to dress. Following the manual examination there may also be an examination of strength, motor control, and overall biomechanics and neuromuscular control. The physical and occupational therapists will then communicate the findings to the patient and together with their patient they establish an assessment, short term and long term goals and a treatment plan. Typically people with pelvic floor dysfunction are seen one time per week for one hour for varying amounts of time based on the severity and chronicity of the disease. A home exercise program will be established and the physical and occupational therapists will help coordinate other providers on the treatment team. Typically patients are seen for 3 months to a year.
What is pudendal neuralgia and how is it treated?
Pudendal Neuralgia is a clinical diagnosis that means pain in the sensory distribution of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is a mixed nerve that exits the S2 – S4 sacral nerve roots, we have a right and left pudendal nerve and each side has three main trunks: the dorsal branch, the perineal branch, and the inferior rectal branch. The branches supply sensation to the clitoris/penis, labia/scrotum, perineum, anus, the distal ⅓ of the urethra and rectum, and the vulva and vestibule. The nerve branches also control the pelvic floor muscles. The pudendal nerve follows a tortuous path through the pelvic floor and girdle, leaving it vulnerable to compression and tension injuries at various points along its path.
Pudendal Neuralgia occurs when the nerve is unable to slide, glide and move normally and as a result, people experience pain in some or all of the above-mentioned areas. Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy plays a crucial role in identifying the mechanical impairments that are affecting the nerve. The physical and occupational therapy treatment plan is designed to restore normal neural function. Patients with pudendal neuralgia require pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from medical management that includes pharmaceuticals and procedures such as pudendal nerve blocks or botox injections.
What is interstitial cystitis and how is it treated?
Interstitial Cystitis is a clinical diagnosis characterized by irritative bladder symptoms such as urinary urgency, frequency, and hesitancy in the absence of infection. Research has shown the majority of patients who meet the clinical definition have pelvic floor dysfunction and myalgia. Therefore, the American Urologic Association recommends pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy as first-line treatment for Interstitial Cystitis. Patients will benefit from pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from pharmacologic management or medical procedures such as bladder instillations.
Who is the Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Team?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center was founded by Elizabeth Akincilar and Stephanie Prendergast in 2006, they have been treating people with pelvic floor disorders since 2001. They were trained and mentored by a medical doctor and quickly became experts in treating pelvic floor disorders. They began creating courses and sharing their knowledge around the world. They expanded to 11 locations in the United States and developed a residency style training program for their employees with ongoing weekly mentoring. The physical and occupational therapistss who work at PHRC have undergone more training than the majority of pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss and as a result offer efficient and high quality care.
How many years of experience do we have?
Stephanie and Liz have 24 years of experience and help each and every team member become an expert in the field through their training and mentoring program.
Why PHRC versus anyone else?
PHRC is unique because of the specific focus on pelvic floor disorders and the leadership at our company. We are constantly lecturing, teaching, and staying ahead of the curve with our connections to medical experts and emerging experts. As a result, we are able to efficiently and effectively help our patients restore their pelvic health.
Do we treat men for pelvic floor therapy?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center is unique in that the Cofounders have always treated people of all genders and therefore have trained the team members and staff the same way. Many pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss focus solely on people with vulvas, this is not the case here.
Do I need pelvic floor therapy forever?
The majority of people with pelvic floor dysfunction will undergo pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy for a set amount of time based on their goals. Every 6 -8 weeks goals will be re-established based on the physical improvements and remaining physical impairments. Most patients will achieve their goals in 3 – 6 months. If there are complicating medical or untreated comorbidities some patients will be in therapy longer.
By PHRC Admin & Co-Author Cecilia Plaza, J.D
Have you listened to The Retrievals podcast series?
In a world where pain is subjective, women often find themselves marginalized, dismissed, and even ignored when it comes to their own experiences of pain. This issue has recently been brought to light through a thought-provoking podcast called “The Retrievals,” hosted by Susan Burton, which explores the systemic dismissal of women’s pain within the medical field. In this blog post, we will delve into the revelations shared by the podcast and shed light on the urgent need for change.
The podcast, “The Retrievals,” sheds light on the challenges faced by women when seeking adequate pain control during medical procedures and shares stories from women who underwent IVF egg retrievals without adequate pain control.
The Dismissal of Women’s Pain:
“The Retrievals” podcast serves as a powerful platform to amplify the voices of women who have undergone IVF egg retrieval without proper pain control. Shockingly, these women’s pain was exacerbated by a nurse diverting their medication, leaving them in excruciating discomfort. This series revealed the truth behind Yale’s fertility clinic and their involvement and handling of one of their nurses swapping saline for fentanyl in these procedures. The journalist raises the question of why we do not trust our patients more, especially when it comes to pain. hy did no one intervene or stop the procedure when the patient was clearly in extreme pain? Why was the patient’s pain minimized and not believed? How did this happen, over and over, to so many women?
Systemic Minimization of Women’s Pain:
Unfortunately, the dismissal of women’s pain is not an isolated incident. It is a systemic issue deeply ingrained within the medical profession. Many medical practitioners tend to think of women as being more emotional, irrational, and “hysterical” than men, leading practitioners to believe that women patients exaggerate their symptoms. As a result, they’re treated less seriously, and, on average, receive less screening, testing, and treatment than men. Women of color, particularly Black women, face even more extreme dismissal of their pain, highlighting the intersectionality of this problem. There is a pervasive myth, still believed by some, that Black patients, and Black women in particular, are less able to feel pain than White patients. Finally, the racist and misogynistic history of government control over reproduction, from 1900s eugenics to present-day birth control restrictions, has left the medical system primed to view women as vessels, prioritizing their reproductive function over their overall well-being.
Gender Bias and Its Consequences:
The podcast sheds light on the gender bias that permeates the medical profession. Doctors often assume that women seek treatment solely for eventual pregnancy, neglecting other aspects of their health and well-being. Women’s worth is all too frequently tied to their reproductive capacity, leaving little room for acknowledgment of their pain and trauma.
Inequality in Medical Care:
Women’s pain is not treated equally because women are not treated equally. Suing for malpractice due to subpar treatment is often more difficult for women. The standard of care provided to women is lower due to a lack of knowledge about women’s health, symptom presentation, and illnesses that disproportionately affect women, as well as a pervasive distrust and discounting of women patients. This perpetuates their suffering and compromises their overall quality of life. It is crucial to recognize that women are more than mere vessels and that their pain should be taken seriously. This is highlighted in the podcast when Susan Burton stumbles upon an article titled “Miss Diagnosis: Gendered Injustice in Medical Malpractice Law” by Cecilia Plaza, J.D., when asking the question “can you sue for pain?” This article is a must read and identifies and addresses the knowledge gap, as well as the trust gap that has led to the dismissal of women’s pain and gender gaps in medical research and practice.
Paving the Way for Change:
To address this pressing issue, it is essential to challenge sexism within the medical profession and advocate for a paradigm shift in how women’s pain is perceived and treated. Healthcare providers must prioritize women’s pain and trauma, considering their holistic well-being beyond just their reproductive capacity. Finding supportive and understanding healthcare providers can significantly improve a woman’s quality of life during fertility treatments and beyond.
The revelations shared by “The Retrievals” podcast have brought to light the disturbing reality of women’s pain being minimized within the medical system. It is imperative that we recognize the gender bias and systemic flaws that perpetuate this injustice. By amplifying these voices, advocating for equal treatment, and demanding change, we can strive toward a future where women’s pain is acknowledged, validated, and appropriately addressed.
The pod criticizes the medical system for treating women’s bodies as vessels solely for reproduction, prioritizing the goal of having a baby over the overall well-being of women. This is highlighted in the podcast when Susan Burton describes the letter that was sent to women who might have been impacted by the clinic nurse’s diversion of fentanyl and the clinic’s improper handling of opiates, stating that there was “no reason to believe that this event has had any negative effect on your health or the outcome of the care that you received.” It exemplifies the prevalence of sexism in the medical profession, with doctors assuming that women seek treatment solely for eventual pregnancy. The idea that extreme pain, trauma, and betrayal by trusted medical professionals didn’t negatively affect the health of the victims is laughable. And yet, this is the basis of and continues to reproduce lower standards of care and unequal treatment for women, as well as making it harder for them to sue for malpractice after receiving appropriate pain management.
What are your thoughts?
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Are you unable to come see us in person in the Bay Area, Southern California or New England? We offer virtual physical and occupational therapy appointments too!
Virtual sessions are available with PHRC pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss via our video platform, Zoom, or via phone. For more information and to schedule, please visit our digital healthcare page.
Do you enjoy or blog and want more content from PHRC? Please head over to social media!
FAQ
What are pelvic floor muscles?
The pelvic floor muscles are a group of muscles that run from the coccyx to the pubic bone. They are part of the core, helping to support our entire body as well as providing support for the bowel, bladder and uterus. These muscles help us maintain bowel and bladder control and are involved in sexual pleasure and orgasm. The technical name of the pelvic floor muscles is the Levator Ani muscle group. The pudendal nerve, the levator ani nerve, and branches from the S2 – S4 nerve roots innervate the pelvic floor muscles. They are under voluntary and autonomic control, which is a unique feature only they possess compared to other muscle groups.
What is pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy?
Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy is a specialized area of physical and occupational therapy. Currently, physical and occupational therapistss need advanced post-graduate education to be able to help people with pelvic floor dysfunction because pelvic floor disorders are not yet being taught in standard physical and occupational therapy curricula. The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center provides extensive training for our staff because we recognize the limitations of physical and occupational therapy education in this unique area.
What happens at pelvic floor therapy?
During an evaluation for pelvic floor dysfunction the physical and occupational therapists will take a detailed history. Following the history the physical and occupational therapists will leave the room to allow the patient to change and drape themselves. The physical and occupational therapists will return to the room and using gloved hands will perform an external and internal manual assessment of the pelvic floor and girdle muscles. The physical and occupational therapists will once again leave the room and allow the patient to dress. Following the manual examination there may also be an examination of strength, motor control, and overall biomechanics and neuromuscular control. The physical and occupational therapists will then communicate the findings to the patient and together with their patient they establish an assessment, short term and long term goals and a treatment plan. Typically people with pelvic floor dysfunction are seen one time per week for one hour for varying amounts of time based on the severity and chronicity of the disease. A home exercise program will be established and the physical and occupational therapists will help coordinate other providers on the treatment team. Typically patients are seen for 3 months to a year.
What is pudendal neuralgia and how is it treated?
Pudendal Neuralgia is a clinical diagnosis that means pain in the sensory distribution of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is a mixed nerve that exits the S2 – S4 sacral nerve roots, we have a right and left pudendal nerve and each side has three main trunks: the dorsal branch, the perineal branch, and the inferior rectal branch. The branches supply sensation to the clitoris/penis, labia/scrotum, perineum, anus, the distal ⅓ of the urethra and rectum, and the vulva and vestibule. The nerve branches also control the pelvic floor muscles. The pudendal nerve follows a tortuous path through the pelvic floor and girdle, leaving it vulnerable to compression and tension injuries at various points along its path.
Pudendal Neuralgia occurs when the nerve is unable to slide, glide and move normally and as a result, people experience pain in some or all of the above-mentioned areas. Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy plays a crucial role in identifying the mechanical impairments that are affecting the nerve. The physical and occupational therapy treatment plan is designed to restore normal neural function. Patients with pudendal neuralgia require pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from medical management that includes pharmaceuticals and procedures such as pudendal nerve blocks or botox injections.
What is interstitial cystitis and how is it treated?
Interstitial Cystitis is a clinical diagnosis characterized by irritative bladder symptoms such as urinary urgency, frequency, and hesitancy in the absence of infection. Research has shown the majority of patients who meet the clinical definition have pelvic floor dysfunction and myalgia. Therefore, the American Urologic Association recommends pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy as first-line treatment for Interstitial Cystitis. Patients will benefit from pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from pharmacologic management or medical procedures such as bladder instillations.
Who is the Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Team?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center was founded by Elizabeth Akincilar and Stephanie Prendergast in 2006, they have been treating people with pelvic floor disorders since 2001. They were trained and mentored by a medical doctor and quickly became experts in treating pelvic floor disorders. They began creating courses and sharing their knowledge around the world. They expanded to 11 locations in the United States and developed a residency style training program for their employees with ongoing weekly mentoring. The physical and occupational therapistss who work at PHRC have undergone more training than the majority of pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss and as a result offer efficient and high quality care.
How many years of experience do we have?
Stephanie and Liz have 24 years of experience and help each and every team member become an expert in the field through their training and mentoring program.
Why PHRC versus anyone else?
PHRC is unique because of the specific focus on pelvic floor disorders and the leadership at our company. We are constantly lecturing, teaching, and staying ahead of the curve with our connections to medical experts and emerging experts. As a result, we are able to efficiently and effectively help our patients restore their pelvic health.
Do we treat men for pelvic floor therapy?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center is unique in that the Cofounders have always treated people of all genders and therefore have trained the team members and staff the same way. Many pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss focus solely on people with vulvas, this is not the case here.
Do I need pelvic floor therapy forever?
The majority of people with pelvic floor dysfunction will undergo pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy for a set amount of time based on their goals. Every 6 -8 weeks goals will be re-established based on the physical improvements and remaining physical impairments. Most patients will achieve their goals in 3 – 6 months. If there are complicating medical or untreated comorbidities some patients will be in therapy longer.
By PHRC Admin
National Condom Week, celebrated every year from February 14th to 21st, serves as a pivotal reminder of the importance of sexual health and awareness. It provides an opportunity to educate about safe sex practices and their significance in maintaining overall wellbeing. As pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss, understanding the intricate relationship between sexual health and pelvic health is crucial.
The Importance of Condoms
Condoms are more than just a contraceptive method; they are a vital tool in protecting against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)1. Their correct and consistent use can significantly contribute to maintaining sexual health.
Sexual Health and Pelvic Health: An Interconnected Relationship
The connection between sexual health and pelvic health is profound. STIs, for instance, can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, resulting in chronic pelvic pain and potential fertility issues. By promoting condom use and safe sex practices, the risk of such conditions can be minimized, thereby safeguarding pelvic health.
Pelvic Floor Health and Safe Sex
Pelvic pain and dysfunction often stem from sexual activities. Conditions like pelvic inflammatory disease, which can severely affect pelvic health, can be prevented by practicing safe sex. Furthermore, engaging in comfortable, pain-free sexual activity is imperative for maintaining a healthy pelvic floor. If discomfort or pain is experienced during sex, it could be indicative of issues with the pelvic floor muscles. It’s essential to remember that pain isn’t a normal part of sexual activity, and professional help should be sought if discomfort persists.
Education: A Cornerstone of Sexual Health Awareness
Education plays an instrumental role in sexual health. Understanding the different types of contraceptives available, their functionality, and effectiveness can significantly impact sexual health decisions. For instance, when used correctly, condoms are 98% effective. However, their protective qualities against STIs and unintended pregnancies are only effective when used consistently and correctly.
Facilitating Open Conversations About Sexual Health
National Condom Week provides an opportunity to stimulate open conversations about sexual health, dismantle stigmas, and promote a healthy approach to sex. Encouraging such discussions can help identify misconceptions or fears, leading to better understanding, safer practices, and healthier attitudes towards sex.
As National Condom Week is celebrated, it’s important to remember that sexual health forms an integral part of overall health and wellbeing. Prioritizing sexual health, not just during this week, but throughout the year, contributes significantly to maintaining pelvic health. Safe sex is healthy sex, and awareness is key to promoting and maintaining sexual health at its optimum.
Sources:
- National Condom Week – February 14-21, 2024
- CDC | Condom Effectiveness
- STD Awareness Week General Resources | STDs
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Are you unable to come see us in person in the Bay Area, Southern California or New England? We offer virtual physical and occupational therapy appointments too!
Virtual sessions are available with PHRC pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss via our video platform, Zoom, or via phone. For more information and to schedule, please visit our digital healthcare page.
Do you enjoy or blog and want more content from PHRC? Please head over to social media!
FAQ
What are pelvic floor muscles?
The pelvic floor muscles are a group of muscles that run from the coccyx to the pubic bone. They are part of the core, helping to support our entire body as well as providing support for the bowel, bladder and uterus. These muscles help us maintain bowel and bladder control and are involved in sexual pleasure and orgasm. The technical name of the pelvic floor muscles is the Levator Ani muscle group. The pudendal nerve, the levator ani nerve, and branches from the S2 – S4 nerve roots innervate the pelvic floor muscles. They are under voluntary and autonomic control, which is a unique feature only they possess compared to other muscle groups.
What is pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy?
Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy is a specialized area of physical and occupational therapy. Currently, physical and occupational therapistss need advanced post-graduate education to be able to help people with pelvic floor dysfunction because pelvic floor disorders are not yet being taught in standard physical and occupational therapy curricula. The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center provides extensive training for our staff because we recognize the limitations of physical and occupational therapy education in this unique area.
What happens at pelvic floor therapy?
During an evaluation for pelvic floor dysfunction the physical and occupational therapists will take a detailed history. Following the history the physical and occupational therapists will leave the room to allow the patient to change and drape themselves. The physical and occupational therapists will return to the room and using gloved hands will perform an external and internal manual assessment of the pelvic floor and girdle muscles. The physical and occupational therapists will once again leave the room and allow the patient to dress. Following the manual examination there may also be an examination of strength, motor control, and overall biomechanics and neuromuscular control. The physical and occupational therapists will then communicate the findings to the patient and together with their patient they establish an assessment, short term and long term goals and a treatment plan. Typically people with pelvic floor dysfunction are seen one time per week for one hour for varying amounts of time based on the severity and chronicity of the disease. A home exercise program will be established and the physical and occupational therapists will help coordinate other providers on the treatment team. Typically patients are seen for 3 months to a year.
What is pudendal neuralgia and how is it treated?
Pudendal Neuralgia is a clinical diagnosis that means pain in the sensory distribution of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is a mixed nerve that exits the S2 – S4 sacral nerve roots, we have a right and left pudendal nerve and each side has three main trunks: the dorsal branch, the perineal branch, and the inferior rectal branch. The branches supply sensation to the clitoris/penis, labia/scrotum, perineum, anus, the distal ⅓ of the urethra and rectum, and the vulva and vestibule. The nerve branches also control the pelvic floor muscles. The pudendal nerve follows a tortuous path through the pelvic floor and girdle, leaving it vulnerable to compression and tension injuries at various points along its path.
Pudendal Neuralgia occurs when the nerve is unable to slide, glide and move normally and as a result, people experience pain in some or all of the above-mentioned areas. Pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy plays a crucial role in identifying the mechanical impairments that are affecting the nerve. The physical and occupational therapy treatment plan is designed to restore normal neural function. Patients with pudendal neuralgia require pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from medical management that includes pharmaceuticals and procedures such as pudendal nerve blocks or botox injections.
What is interstitial cystitis and how is it treated?
Interstitial Cystitis is a clinical diagnosis characterized by irritative bladder symptoms such as urinary urgency, frequency, and hesitancy in the absence of infection. Research has shown the majority of patients who meet the clinical definition have pelvic floor dysfunction and myalgia. Therefore, the American Urologic Association recommends pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy as first-line treatment for Interstitial Cystitis. Patients will benefit from pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy and may also benefit from pharmacologic management or medical procedures such as bladder instillations.
Who is the Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Team?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center was founded by Elizabeth Akincilar and Stephanie Prendergast in 2006, they have been treating people with pelvic floor disorders since 2001. They were trained and mentored by a medical doctor and quickly became experts in treating pelvic floor disorders. They began creating courses and sharing their knowledge around the world. They expanded to 11 locations in the United States and developed a residency style training program for their employees with ongoing weekly mentoring. The physical and occupational therapistss who work at PHRC have undergone more training than the majority of pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss and as a result offer efficient and high quality care.
How many years of experience do we have?
Stephanie and Liz have 24 years of experience and help each and every team member become an expert in the field through their training and mentoring program.
Why PHRC versus anyone else?
PHRC is unique because of the specific focus on pelvic floor disorders and the leadership at our company. We are constantly lecturing, teaching, and staying ahead of the curve with our connections to medical experts and emerging experts. As a result, we are able to efficiently and effectively help our patients restore their pelvic health.
Do we treat men for pelvic floor therapy?
The Pelvic Health and Rehabilitation Center is unique in that the Cofounders have always treated people of all genders and therefore have trained the team members and staff the same way. Many pelvic floor physical and occupational therapistss focus solely on people with vulvas, this is not the case here.
Do I need pelvic floor therapy forever?
The majority of people with pelvic floor dysfunction will undergo pelvic floor physical and occupational therapy for a set amount of time based on their goals. Every 6 -8 weeks goals will be re-established based on the physical improvements and remaining physical impairments. Most patients will achieve their goals in 3 – 6 months. If there are complicating medical or untreated comorbidities some patients will be in therapy longer.



